Vitamin B: How To Use It For Your Benefit
Vitamin B is the collective name of a group of eight water-soluble vitamins. Some of the most important being Vitamin B12, B6, and B9 (folic acid). They are a family of vitamins belonging to the group water-soluble vitamins.
If you are looking for a specific B vitamin, I recommend you use the expanded toc to find it.
Table of Contents
Why Do We Need Vitamin B
B vitamins are involved in the processing of carbohydrates and fats for energy production.
The B vitamins are vital for neural function ◳, especially vitamins B6, B12, and folate.
We need vitamin B for the metabolism of cells and the formation of blood cells. The body needs vitamin B for protein metabolism.
Vitamin B ensures that new cells and red blood cells can be formed, which in turn reduces the risk of anemia.
Vitamin B Deficiency
Vitamin B deficiency is associated with anxiety ◳, malaise, and depression.
Vitamin B deficiency is relatively common and can affect anyone. Especially the elderly, pregnant, and vegans are people that are at risk for developing a vitamin B deficiency.
It can take several years before symptoms of vitamin B deficiency are noticing. That is why you must contact your physician if you suspect that you are at risk.
All Our Articles On Vitamin B
Below you will find information about all B Vitamins.
Biotin (Vitamin B7)
Biotin is necessary for the metabolism of protein, fats, and carbohydrates. Learn more about biotin in What Is Biotin & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Deficiency can lead to muscle pain, heart problems, anemia, and depression. See what kind of benefit biotin has in Biotin: One Research-Backed Benefit
Inositol (Vitamin B8)
Inositol works together with choline, vitamin B6 and taurine to break down fat in the body. You can find more information in What Is Inositol?
It can also positively affect the neurotransmitters in your brain. See more about in Inositol: One Research-Backed Benefit
Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Hundreds of enzymes in the body require niacin. Niacin is needed to break down fats, carbohydrates, and protein. Find out more about niacin in What Is Niacin & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Niacin helps keep the nervous system functioning and the skin healthy. Niacin has many health benefits but also a side-effect. See them in Niacin: 9 Research-Backed Benefits & One Side-Effect
Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5)
Pantothenic acid makes coenzyme A in your body. See more information about it and the research behind it in What Is Pantothenic Acid & What Foods Can I Find It In?
It’s necessary for energy production and the formation of hormones. Pantothenic acid also helps to break down fats, and in other metabolic functions. You can read about the benefits of pantothenic acid in Pantothenic acid: 6 Research-Backed Benefits
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
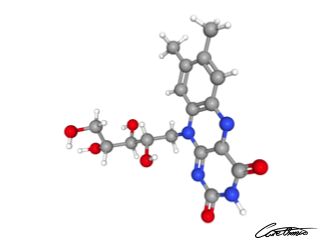
Riboflavin is a vital compound of a healthy diet and is widely distributed in animal and vegetable foods. One problem is that ultraviolet, UV, light can destroy riboflavin.
Learn more about riboflavin in What Is Riboflavin & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Riboflavin possesses many health benefits. If you are interested in knowing more about them, you can go to Riboflavin: 11 Research-Backed Benefits and check them out.
Thiamin (Vitamin B1)
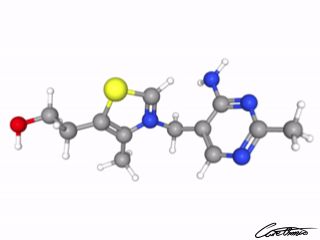
Thiamin functions in the body in the form of thiamin pyrophosphate. Read more about thiamin in What Is Thiamin & What Foods Can I Find It In?
The requirement for thiamin directly correlates with carbohydrate intake. You can find benefits of thiamin in Thiamin: 5 Research-Backed Benefits
Vitamin B6
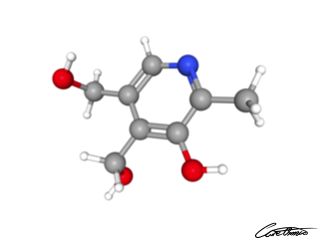
Vitamin B6 is widely studied for its role in disease prevention. You can find more information in What Is Vitamin B6 & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Older adults need more vitamin B6 than younger adults to reduce high plasma homocysteine levels. You can read about more benefits in Vitamin B6: 9 Research-Backed Benefits
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is needed for the body to be able to form red blood cells. If you have too little B12, you might get anemia.
You can find more information about vitamin B12 in What Is Vitamin B12 & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Vitamin B12 is synthesized from bacteria and is found only in animal foods such as meats, milk and milk products, and eggs.
Look at all the benefits of vitamin B12 in Vitamin B12: 6 Research-Backed Benefits
Added Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is often added to fortified foods and found in dietary supplements. It’s a synthetic form of vitamin B12.
Read more about added vitamin B12 in What Is Added Vitamin B12 & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Folate And Folic Acid, (Vitamin B9)
Vitamin B9 is called folic acid, folate, or folinic acid. Together, they are commonly called just folate.
Folate is a water-soluble vitamin, which is vital for the formation of proteins and normal cell division.
Check out information about all folates, their benefits, side-effects, and the research behind them in Folates: How To Use Them For Your Benefit
