Sugars: How To Use Them For Your Benefit
Sugars are simple carbohydrates. It chemically refers to a group of compounds comprising carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
There are two forms of carbohydrates, simple and complex carbohydrates.
The main difference between simple and complex carbohydrates ◳ is; simple carbohydrates digest quickly and are absorbed by the body, where complex carbohydrates take time to digest.
If you are looking for a specific sugar, I recommend you use the expanded toc to find it.
Tip! Use the "Show Expanded TOC" button if you want to jump straight to a specific sugar article.
Table of Contents
Eat A Whole Fruit, Skip The Juice
Sugar occurs naturally in all foods that contain carbohydrates, such as fruits and vegetables, grains, and dairy. Consuming whole foods that contain natural sugar is usually okay.
That is if you eat the whole fruit or vegetable because they also have high amounts of fiber and other beneficial nutrients, which helps the body handle the sugar.
Drinking fruit juice ◳ where the fibers have been taken out, compares to drinking a glass of liquid sugar. Especially if there is added sugar to the drink as well.
The Bad Added Sugar
Most health authorities agree that overconsumption of added sugars, and particularly sugar-sweetened drinks, has contributed to the obesity epidemic.
Consuming too much added sugar might raise blood pressure, increase chronic inflammation, diabetes, and fatty liver disease. These are all linked to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
All Our Articles About Sugar
Below you will find different kinds of sugars. You can find out what they are and what they might be able to do for you, or why you should avoid them.
Fructose or Fruit sugar
Fructose is found in modern diets and used as a sweetener in a variety of food items. Fructose also occurs naturally in abundance in fruits and lesser amounts in tuberous vegetables such as onions and potatoes.
Learn more about fructose in our article: What Is Fructose & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Fructose might not always be the best choice to consume. It has several side-effects. See what they are in our article: Fructose: 5 Research-Backed Side-Effects
Galactose
Galactose is a monosaccharide and has the same chemical formula as glucose. Interested in knowing more? Go to our article: What Is Galactose & What Foods Can I Find It In?
The largest dietary source of galactose is lactose. Lactose is found in milk and products thereof.
Galactose has several benefits find what they are in our article: Galactose: 4 Research-Backed Benefits
Glucose or Dextrose
Glucose's commercial name is dextrose. Glucose is produced by the body in sufficient amounts, meaning it’s non-essential. Learn more about glucose in our article: What Is Glucose & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Glucose is a primary energy source for various tissues, including the brain. But to consume glucose might not be a good idea. See what kind of side-effects it might provide: Glucose: 3 Research-Backed Side-Effects
Lactose or Milk sugar
Lactose is the sugar you find in milk and other dairy products. It’s a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose.
Do you know that not everyone should consume lactose? Learn about it in our article: What Is Lactose & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Lactose intolerance, which is the inability to digest lactose, is quite common. There are some side-effects to consuming lactose, but also benefits. Check them out in our article: Lactose: 3 Research-Backed Benefits & 2 Side-Effects
Maltose or Malt sugar
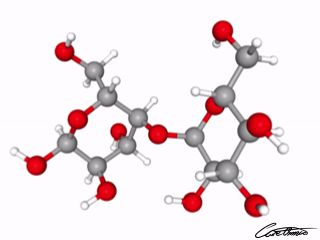
Maltose is an intermediate in the intestinal digestion of glycogen and starch and is found in germinating grains.
Learn more about this sugar and what its uses are in our article: What Is Maltose & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Uses of maltose-containing syrups can be in brewing, baking, soft drink, canning, confectionery, and other food industries.
Consuming maltose in large amounts is not healthy for you. read about the side-effects maltose have in our article: Maltose: 3 Research-Backed Side-Effects
Ribose
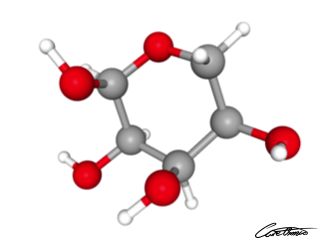
Ribose is a sugar that does not work as the common sugars.
But what is it then? Learn in our article: What Is Ribose?
Ribose is produced in the body and found in all RNA molecules.
But what benefits might it provide for you? See for yourself in our article: Ribose: 2 Research-Backed Benefits
Sorbitol
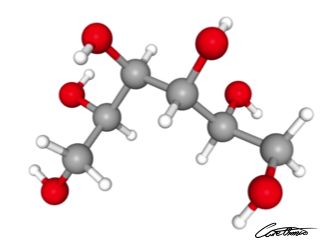
Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol found in some berries and fruits. It also formed in small amounts in the body. Starch can synthetically produce sorbitol. Find out more about sorbitol in our article: What Is Sorbitol?
Sorbitol is not energy-free, and it has a laxative effect at high consumption. That is a side-effect of sorbitol, but it also possesses benefits. What they are, you can find out in our article: Sorbitol: 3 Research-Backed Benefits & One Side-Effect
Sucrose or Common sugar
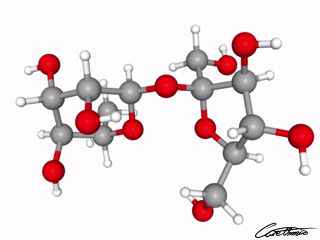
Sucrose is also known as cane sugar or saccharose but is most commonly known as sugar.
Most of us consume way too much sugar daily. For our health, we should try to cut down. If you are interested in knowing more about sucrose, go to our article: What Is Sucrose & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Sucrose is the most abundant disaccharide in nature. Sucrose interacts with food ingredients and in processed foods in many different ways.
Even though sucrose is abundant in nature, does not mean that it will do you good. Sucrose possesses many side-effects that you might want to avoid. Learn about them in our article: Sucrose: One Research-Backed Benefit & 9 Side-Effects
Xylitol or Birch sugar
Xylitol is also called birch sugar. It is a natural sweetener, originally from birches.
What is this natural sweetener that comes from trees? Find out in our article: What Is Xylitol?
It seems to have many advantages over both sugar and artificial sweeteners, is still mostly used in beverages and chewing gum.
Xylitol has both benefits and side-effects that are good to know. See what they are in our article: Xylitol: 2 Research-Backed Benefits & 2 Side-Effects
Added sugar
According to FDA: Added sugars include sugars that are added during the processing of foods, foods packaged as sweeteners, sugars from syrups and honey, and sugars from concentrated fruit or vegetable juices. They do not include naturally occurring sugars in milk, fruits, and vegetables.
Learn more about added sugar and why you should stay away from it in our article: What Is Added Sugar?
Sugar alcohols
Sugar alcohols are also known as polyols. It can be found naturally in fruits and vegetables. Read more about it and find out the names of different sugar alcohols in What Are Sugar Alcohols?
Sugar according to NLEA
Sugar has not always been listed on the Nutrition label. Find out why and what it means in What Are Sugars According To NLEA?
Total count of sugar
On the Nutrition label are sugar listed nowadays. It has not always been that way. When there is a total count of sugars listed, does it mean that all kinds of sugar in the product are in the same post. So you can tell the difference of what kind of sugar the product contain. Read more in What Does Total Count Of Sugars, Including NLEA Mean?.
