Monounsaturated cis Fatty Acids: How To Use Them For Your Benefit
The cis isomer is the natural and the common configuration of unsaturated fatty acids. A fatty acid in a cis configuration is two hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double bond are on the same side of the chain.
cis-Monounsaturated fatty acids are one of four categories among monounsaturated fatty acids.
Tip! If you are looking for a specific cis-monounsaturated fatty acid, I recommend you use the expanded toc to find it.
Table of Contents
Structure Of cis-Monounsaturated Fatty Acids
Most unsaturated fatty acids that occur in nature have their bonds in the cis configuration, which means; the same side. Partial hydrogenation of cis-fats can turn some of the fatty acids into a trans variety, meaning; opposite sides.
Is There Benefits Of cis-Monounsaturated Fatty Acids?
Research show a correlation between cis-monounsaturated fatty acids (cis-MUFAs) and coronary heart disease (CHD). But the effects are not fully understood.
cis-MUFAs may have a role in cardiovascular health ◳. More research is needed to clarify this.
Our Articles About Common cis-Monounsaturated Fatty Acids
Below you will find the most common cis-monounsaturated fatty acids. You can find out what they are and what they might be able to do.
cis-9-Tetradecenoic acid (14:1 c) mostly found in seed oil
cis-9-tetradecenoic acid is only found in low quantities in foods and in nature. You can find some more information about cis-9-tetradecenoic acid in What Is cis-9-Tetradecenoic Acid (14:1 c) & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Palmitoleate (16:1 c) is anti-inflammatory
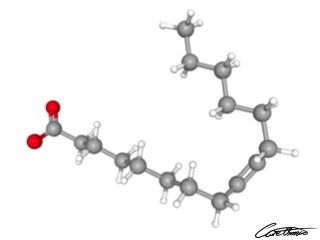
Macadamia nuts and buckthorn seed oil contain palmitoleate. Read more about palmitoleate in What Is Palmitoleate (16:1 c) & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Palmitoleate seems to have the ability to decrease inflammatory activity when it is interacting with specific proteins. Check it out in Palmitoleate (16:1 c): One Research-Backed Benefit
cis-10-Heptadecenoic acid (17:1 c) have no research-backed benefits
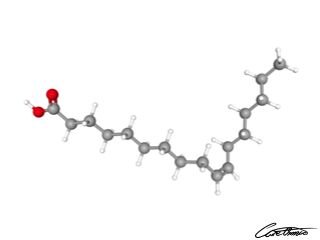
cis-10-Heptadecenoic acid might have potential antitumor activity, but research is still not done on the subject. Find more information about cis-10-heptadecenoic acid in What Is cis-10-Heptadecenoic Acid (17:1 c) & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Oleate (18:1 c) for your digestive tract
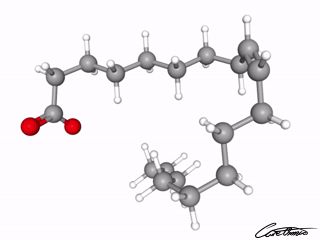
Oleate is common in nature. You can find some more information about oleate in What Is Oleate (18:1 c) & What Foods Can I Find It In?
It seems to have the ability to help keep your digestive tract healthy. Look at its benefit in Oleate (18:1 c): One Research-Backed Benefit
cis-13-Eicosenoic acid (20:1 c) is a neutral acid
cis-13-eicosenoic acid is a relativley neutral acid that is found mostly in fats and oils. Read more in cis-13-Eicosenoic Acid (20:1 c): Remarkably Unique
cis-Erucic acid (22:1 c) might not be good for you
cis-Erucic acid may hold the same side effects that Erucic acid, like it, can be harmful to children. Health concerns about cis-Erucic acid and Erucic acid are still disputed
You can find more information about cis-erucic acid in What Is cis-Erucic Acid (22:1 c) & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Nervonic acid (24:1 c) needed for your brain
Nervonic acid consists of choline, sphingosine, and phosphoric acid. Learn more in What Is Nervonic Acid (24:1 c) & What Foods Can I Find It In?
Nervonic acid has a close relationship with brain development. It may even enhance brain functions.
If you don’t have enough nervonic acid, the risk for obesity-related risk factors will increase. You can find more information about the benefits in Nervonic Acid (24:1 c): 2 Research-Backed Benefits
